PLC Engineering Solutions
We have been offering global turnkey automation solutions for the last 18 years, having 60 installed bases in more than 30 countries. Our range of services includes PLC software development, onsite commissioning & customer service support, with MAPP as an IIoT solution we help to reduce operating and maintenance costs and achieve maximum ROI
PLC, SCADA & Drives Engineering

We develop Control Software as per customer requirements keeping in mind the applicable standards for development and testing. Our experienced team specializes mainly in Software Development for high-quality Siemens and Allen Bradley PLC. We also provide virtual commissioning using simulation software to reduce onsite commissioning time by up to 40%.
Effective Communication between Man and Machine, Let Your Machines do the talking. At KNEO, we believe in establishing a strong foundation for your automation journey.
key neo offerings
- End-to-end projects from concept design and pre-production, to final handover.
- Customized Control Software Development.
- Preparation and review of E-plan Project Design.
- Complete ownership of Automation activities.
- Architecture, Planning, Design, Development & Commissioning of entire control system.
- Evaluation and Implementation of Safety Matrix.
- Virtual Commissioning and Simulation.
Automated Storage and Retrieval System (Warehouse Management)
Digitalize, Visualize and Analyze
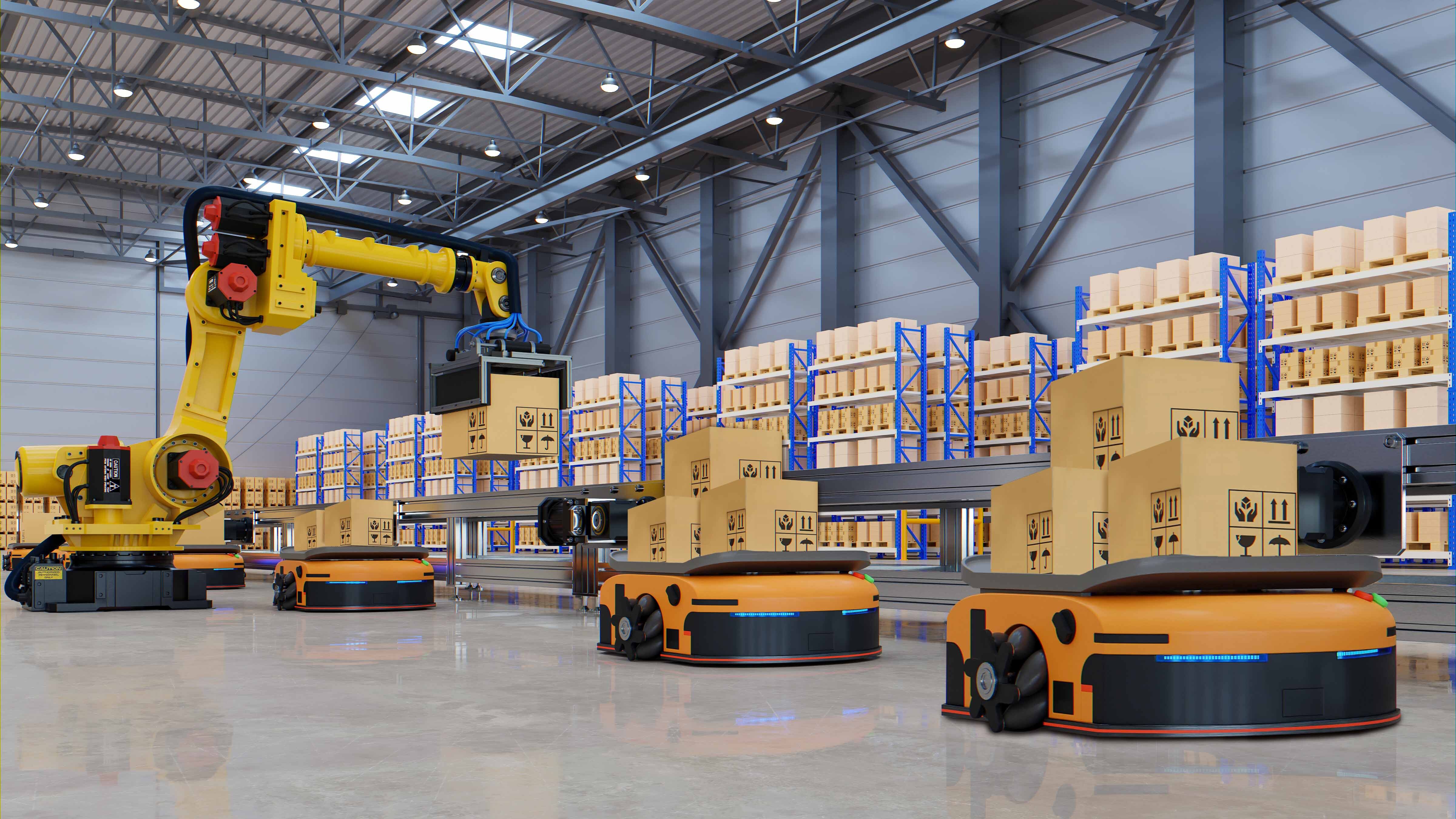

Our MAPP- Warehouse IIOT Platform Solution highlights are:
- Multi PLC Interface and Communication
- Database Management
- Inventory Management
- Wifi and Barcode system
- Product and Pallet Information
- Picking and Packing
Application Areas:
- Receiving Unit
- Storage Unit
- Sorting Unit
- Gripper System
- Stacking Units
- Transfer robots
- AGVs
What we do:
• Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may include material handling, order picking, packing, and shipping.
• Determine the best technology or technologies to use for automation. This may involve evaluating different options, such as robots, conveyors, or AS/RS, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the warehouse.
• Design the layout and flow of the automated warehouse. This includes determining the best location for automation equipment and determining the most efficient routing for materials and products.
• Install and integrate the automation equipment. This may involve installing robotics systems, conveyors, or AS/RS, as well as integrating them with the warehouse’s existing systems, such as the warehouse management system (WMS) and the order management system.
• Providing technical support and training to operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation systems.
• Maintaining and troubleshooting the automation systems to ensure that they are operating at optimal performance.
Our MAPP- Warehouse IIOT Platform Solution highlights are:
- Multi PLC Interface and Communication
- Database Management
- Inventory Management
- Wifi and Barcode system
- Product and Pallet Information
- Picking and Packing
Application Areas:
- Receiving Unit
- Storage Unit
- Sorting Unit
- Gripper System
- Stacking Units
- Transfer robots
- AGVs
Turnkey PLC Automation solution for Dairy Industry
An Ideal Solution for Dairy Industry includes Multi PLC Interface(PLC Services), end-to-end automation line commissioning in various application areas like bottle manufacturing line, buffer storage, Cold storage and warehousing.
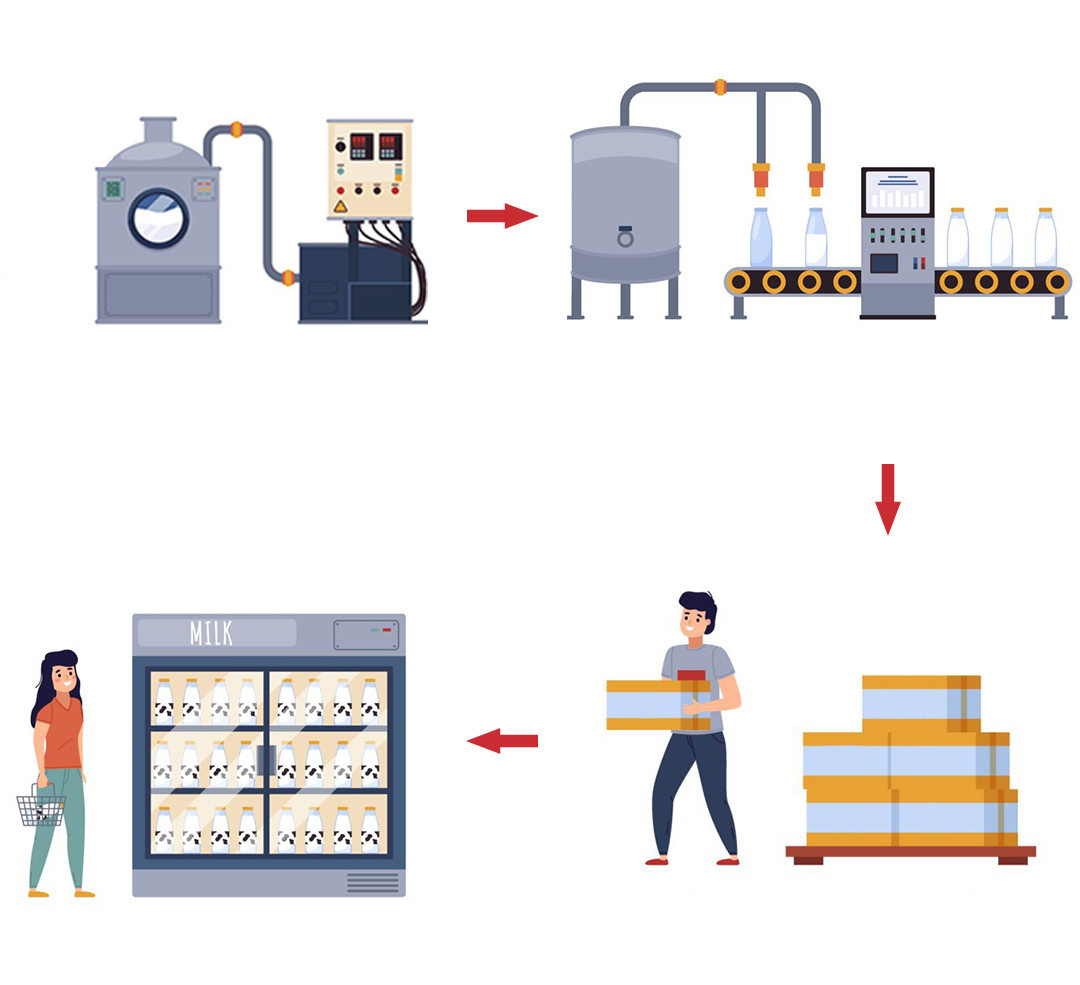
What we do:
- Client Liasoning for long-term project execution and support
- Preparing and reviewing the E-Plan design for the project
- Control software development as per customer standards
- Virtual Commissioning and simulation
- System Architect, planning, design, development and commissioning of the entire system
- Safety Matrix Evaluation and Implementation
Automation Equipment’s
- Palletizing System
- Gantry Robots
- Mould machines and conveyors
Tools & Technology
- Siemens

Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are used in the automobile industry to automate various manufacturing and assembly processes. PLCs are typically used to control and coordinate the operations of machinery and equipment on a factory floor, such as conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other automated systems.
What we do :
- Identify the process or system that needs to be automated. This could be a manufacturing process, such as welding or painting, or it could be a material handling system, such as a conveyor belt.
- Determine the specific tasks and operations that need to be performed by the PLC. This includes identifying the inputs (e.g., sensors) and outputs (e.g., actuators) that the PLC will need to control.
- Design the control logic for the PLC. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Test and debug the PLC program to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Installing and wiring PLC systems and associated input/output devices, such as sensors and actuators.
- Maintaining and troubleshooting PLC systems to ensure that they are operating at optimal performance.
- Providing technical support and training to operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain PLC systems.
- Collaborating with other engineering teams, such as mechanical and electrical engineering teams, to ensure that automation systems are integrated effectively with other systems in the facility.
- We keep up to date with the latest developments in automation technology and industry best practices.
Benefits:
- Improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes, and reduce the need for manual labor.
- Monitor and control safety systems and provide real-time data for process optimization and quality control.
Automation is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes, and to ensure the consistent quality of drug products . Automation can be used to control and coordinate various manufacturing processes, such as mixing, milling, granulating, and tablet pressing.
What we do :
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as robots, conveyors, or automated testing equipment, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the layout and flow of the automated facility. This includes determining the best location for automation equipment and determining the most efficient routing for materials and products.
- Install and integrate the automation equipment. This may involve installing robotics systems, conveyors, or automated testing equipment, as well as integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system
- Designing and programming control systems using software such as PLCs (programmable logic controllers) and SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) systems
- Developing and maintaining process control strategies to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
- Test and debug the automated systems to ensure that they are functioning correctly.
- Collaborating with other engineering and technical staff to troubleshoot and resolve issues with control systems
- Performing system commissioning and validation to ensure that control systems are functioning correctly and in compliance with regulatory standards
- Conducting risk assessments and developing risk management plans to ensure the safety of the production process
- Maintaining documentation related to control systems, including technical manuals, schematics, and validation reports
Train employees on how to use and maintain the automated systems.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of pharmaceutical manufacturing and can help to ensure that drug products meet the required quality standards.
Automation is widely used in process industries, such as chemical, petrochemical, and oil and gas, to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes and to increase the consistency and quality of the end products.
What we do :
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCSs), or process analyzers, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the control logic for the automated system. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Installing and integrating automation equipment, such as PLCs, DCSs, or process analyzers, and integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- Testing and debugging the automation systems to ensure that they are functioning correctly.
- Providing technical support and training to operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation systems.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of process industry manufacturing and can help to ensure that end products meet the required quality standards.
Automation is widely used in the food and beverage industry to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes and to increase the consistency and quality of the end products.
What we do:
- We have gained good experience on end-to-end processes and equipment used in F&B plants from reception to dispatch.
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotic systems, or automated packaging and labeling equipment, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the control logic for the automated system. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Installing and integrating automation equipment, such as PLCs, robotic systems, or automated packaging and labeling equipment, and integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- Test and debug the automation system to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Maintaining and troubleshooting the automation systems to ensure that they are operating at optimal performance.
- Train operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation system.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of food and beverage manufacturing and can help to ensure that end products meet the required quality standards
Automation is used in the textile industry to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes and to increase the consistency and quality of the end products.
What we do:
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotic systems, or automated finishing equipment, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the control logic for the automated system. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Installing and integrating automation equipment, such as PLCs, robotic systems, or automated finishing equipment, and integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- Install and wire the automation equipment. This involves connecting the automation equipment to the process equipment and any sensors and actuators that are needed.
- Test and debug the automation system to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Train operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation system.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of textile manufacturing and can help to ensure that end products meet the required quality standards.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are used in the automobile industry to automate various manufacturing and assembly processes. PLCs are typically used to control and coordinate the operations of machinery and equipment on a factory floor, such as conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other automated systems.
What we do :
- Identify the process or system that needs to be automated. This could be a manufacturing process, such as welding or painting, or it could be a material handling system, such as a conveyor belt.
- Determine the specific tasks and operations that need to be performed by the PLC. This includes identifying the inputs (e.g., sensors) and outputs (e.g., actuators) that the PLC will need to control.
- Design the control logic for the PLC. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
Automation is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes, and to ensure the consistent quality of drug products . Automation can be used to control and coordinate various manufacturing processes, such as mixing, milling, granulating, and tablet pressing.
What we do :
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as robots, conveyors, or automated testing equipment, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the layout and flow of the automated facility. This includes determining the best location for automation equipment and determining the most efficient routing for materials and products.
- Install and integrate the automation equipment. This may involve installing robotics systems, conveyors, or automated testing equipment, as well as integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system
- Designing and programming control systems using software such as PLCs (programmable logic controllers) and SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) systems
- Developing and maintaining process control strategies to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
- Test and debug the automated systems to ensure that they are functioning correctly.
- Collaborating with other engineering and technical staff to troubleshoot and resolve issues with control systems
- Performing system commissioning and validation to ensure that control systems are functioning correctly and in compliance with regulatory standards
- Conducting risk assessments and developing risk management plans to ensure the safety of the production process
- Maintaining documentation related to control systems, including technical manuals, schematics, and validation reports
Train employees on how to use and maintain the automated systems.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of pharmaceutical manufacturing and can help to ensure that drug products meet the required quality standards.
Automation is widely used in process industries, such as chemical, petrochemical, and oil and gas, to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes and to increase the consistency and quality of the end products.
What we do :
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCSs), or process analyzers, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the control logic for the automated system. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Installing and integrating automation equipment, such as PLCs, DCSs, or process analyzers, and integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- Testing and debugging the automation systems to ensure that they are functioning correctly.
- Providing technical support and training to operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation systems.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of process industry manufacturing and can help to ensure that end products meet the required quality standards.
Automation is widely used in the food and beverage industry to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes and to increase the consistency and quality of the end products.
What we do:
- We have gained good experience on end-to-end processes and equipment used in F&B plants from reception to dispatch.
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotic systems, or automated packaging and labeling equipment, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the control logic for the automated system. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Installing and integrating automation equipment, such as PLCs, robotic systems, or automated packaging and labeling equipment, and integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- Test and debug the automation system to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Maintaining and troubleshooting the automation systems to ensure that they are operating at optimal performance.
- Train operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation system.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of food and beverage manufacturing and can help to ensure that end products meet the
Automation is used in the textile industry to improve the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes and to increase the consistency and quality of the end products.
What we do:
- Identify the processes and tasks that can be automated. This may involve evaluating the current manufacturing processes and identifying areas where automation could improve efficiency or accuracy.
- Determine the best automation technology to use. This may involve evaluating different options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotic systems, or automated finishing equipment, and deciding which will be the most cost-effective and efficient for the specific needs of the facility.
- Design the control logic for the automated system. This involves creating a program using a specialized programming language, such as Ladder Logic or Structured Text, that specifies the conditions under which certain actions should be taken.
- Installing and integrating automation equipment, such as PLCs, robotic systems, or automated finishing equipment, and integrating them with the facility’s existing systems, such as the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
- Install and wire the automation equipment. This involves connecting the automation equipment to the process equipment and any sensors and actuators that are needed.
- Test and debug the automation system to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Train operators and maintenance staff on how to use and maintain the automation system.
Benefits:
Automation can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of textile manufacturing and can help to ensure that end products meet the required quality standards.
